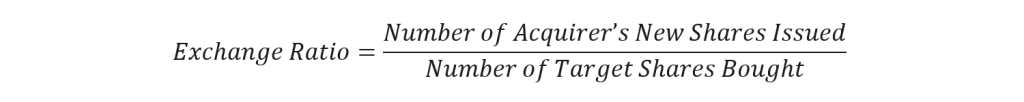Exchange Ratio Template
October 27, 2025
Exchange Ratio Template
An exchange ratio is a key metric used in mergers and acquisitions (M&A) to determine how many shares of the acquiring company will be exchanged for each share of the target company. This ratio ensures that shareholders of the target company receive fair value in the form of shares from the acquiring entity.
How to Calculate an Exchange Ratio?
The exchange ratio is calculated using the following formula:
Exchange Ratio = Number of Acquirer’s New Shares Issued ÷ Number of Target Shares Bought
To determine the number of new shares issued by the acquirer:
Acquirer’s New Shares Issued = Equity Issued to Do the Deal ÷ Acquirer’s Share Price
Example:
- Target company shares: 1,000
- Target share price: $10
- Deal value: $10,000
- Acquirer share price: $5
- Acquirer issues 2,000 shares to finance the deal
- Exchange Ratio = 2,000 ÷ 1,000 = 2:1
This means the acquirer offers 2 shares for every 1 share of the target company.
Download the Free Template
You can download the exchange ratio Excel template at the top of this page. This template includes:
- Step-by-step calculations
- Example scenarios
- Synergy and premium analysis
- Share issuance breakdown
Importance of the Exchange Ratio
The exchange ratio is a vital element in equity-financed mergers and acquisitions, determining how many shares of the acquiring company are offered for each share of the target. It ensures fair value for shareholders and directly affects the ownership structure of the merged entity.
A well-calculated exchange ratio reflects the relative value of both companies and helps structure the deal appropriately.
There are two main types of exchange ratios:
- Fixed Exchange Ratio: The number of shares offered remains constant throughout the deal.
- Floating Exchange Ratio: Adjusts to ensure the target receives a fixed value, regardless of share price fluctuations.
Beyond valuation, the exchange ratio provides transparency for investors, clarifying how the deal is financed and what their post-merger stake will be. Ultimately, it’s a key factor in ensuring fairness, strategic alignment, and stakeholder confidence in the transaction.
Additional Resources
Online Finance Courses
Investment Banking Course
A Day in the Life of an Investment Banking Intern
Investment Banking Interview Skills