Sharpe Ratio Calculator Template
November 19, 2025
What is Sharpe Ratio?
The Sharpe ratio measures the risk-adjusted return of an investment portfolio or asset. It is defined as the portfolio’s excess return (the return above the risk-free rate) divided by its risk, which is measured by the standard deviation of portfolio returns. Sharpe ratio tells you how much additional return you are receiving for the extra volatility that you endure for holding a riskier asset or portfolio.
How to Calculate Sharpe Ratio
To calculate the Sharpe ratio, follow these steps:
- Compute the excess return: Subtract the risk-free rate (often the 90-day treasury bill rate) from the expected return of the portfolio.
- Calculate the standard deviation: Find the standard deviation of the portfolio’s returns, which measures the risk or volatility.
- Divide excess return by standard deviation: The Sharpe ratio is the excess return divided by the standard deviation of the portfolio’s return.
Sharpe Ratio Formula
The Sharpe ratio can be calculated using the following formula:
Sharpe Ratio = (R(P) – R(F)) /Std Dev (P)
R(P): Expected return on portfolio
R(F): Risk-free rate of return
S(P): Standard deviation of portfolio return
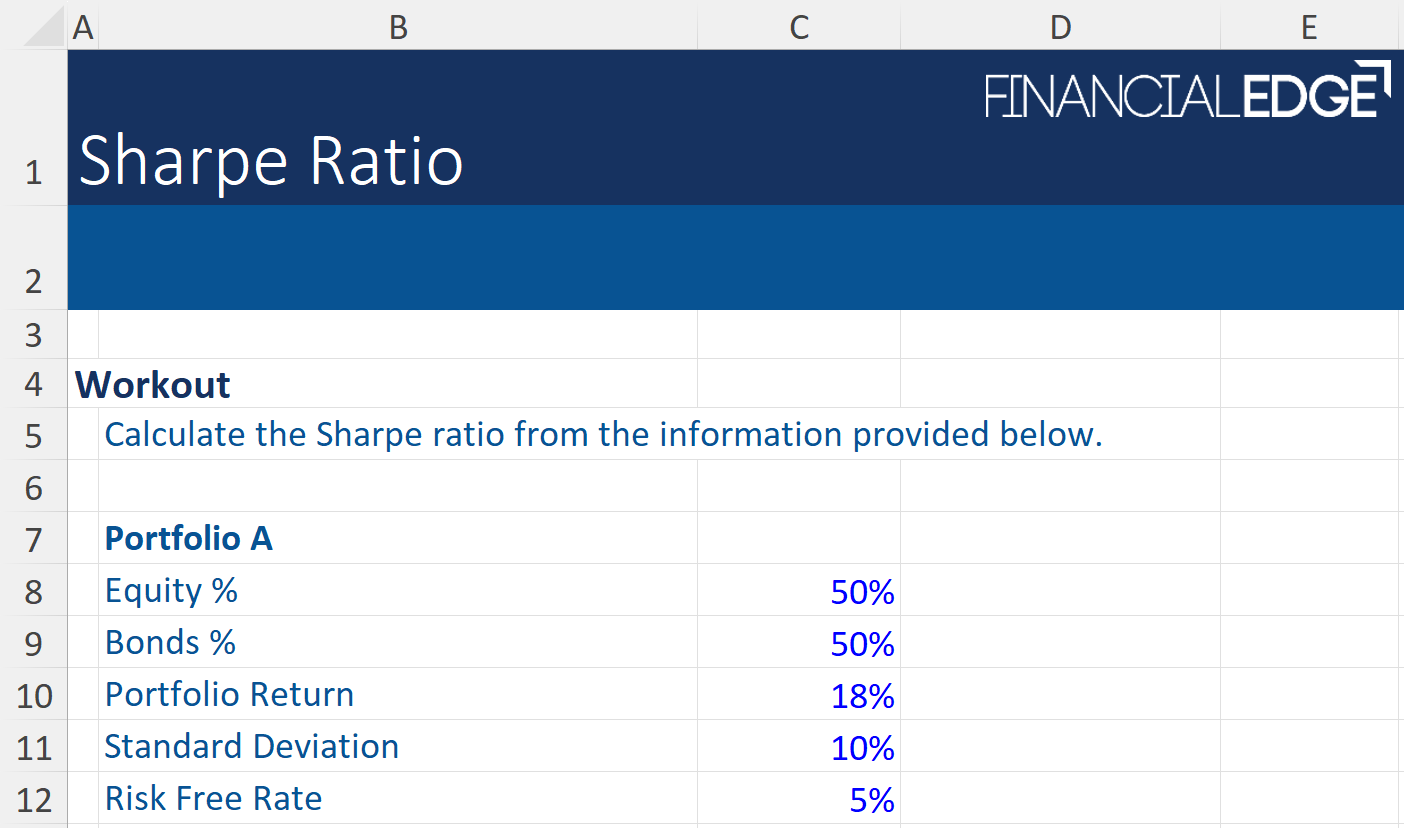
Sharpe Ratio Calculator Template
Download the ready-to-use Sharpe ratio calculator template.
What is a Good Sharpe Ratio?
A higher Sharpe ratio indicates better risk-adjusted performance. Investors generally prefer portfolios with higher Sharpe ratios, as they offer higher returns for each unit of risk taken.
A Sharpe ratio between 1 and 1.99 is considered acceptable or good.
A Sharpe ratio between 2 and 2.99 is considered very good.
A Sharpe ratio of 3 or higher is considered excellent.